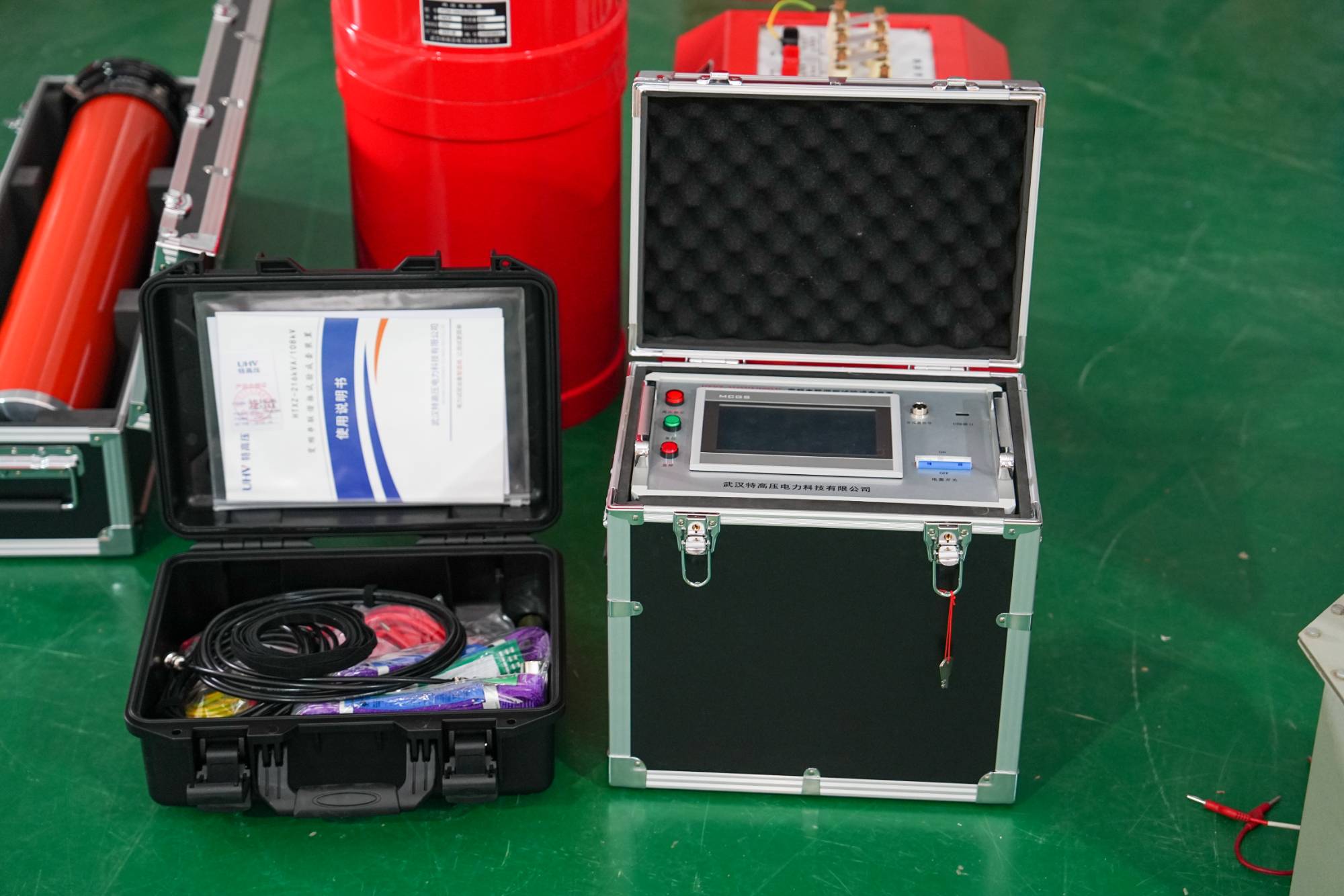
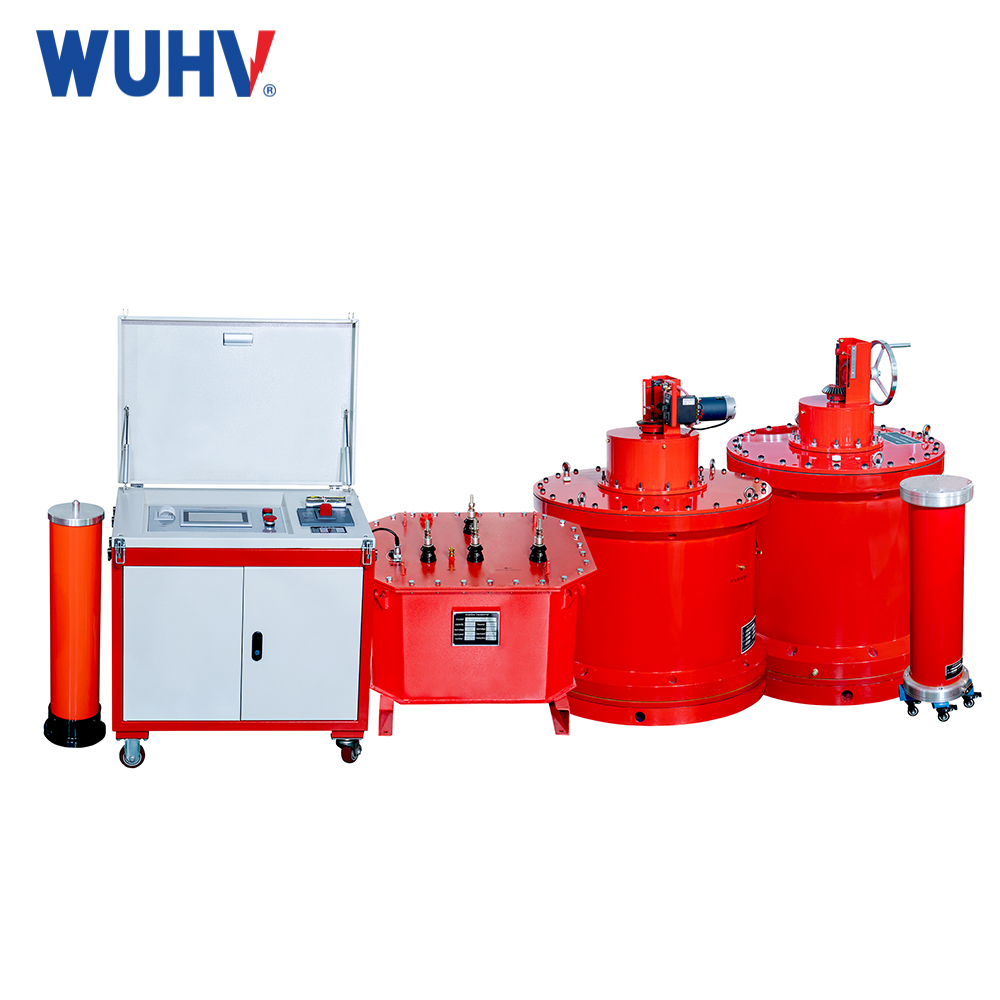
Series resonant intermediate frequency power supply? Wuhan UHV specializes in the production of series resonance, with a wide range of product selection and professional electrical testing. To find series resonance, choose Wuhan UHV.
Introduction to series resonant intermediate frequency power supply
The principle of electromagnetic induction: In 1831, British physicist Faraday discovered the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction and proposed a corresponding theoretical explanation. The content is that when there is an alternating magnetic field in the area surrounded by the circuit, an electromotive force will be induced at both ends of the circuit, and if closed, an induced current will be generated. The principle of induction heating is to generate alternating current, thereby generating an alternating magnetic field, and then using the alternating magnetic field to generate eddy currents to achieve the heating effect.
Skin effect
When an alternating current flows through a conductor, an induced current is generated in the conductor, causing the current to spread towards the surface of the conductor. That is to say, the current density on the surface of the conductor will be greater than the current density at the center. This invisibly reduces the conductive cross-section of the conductor, thereby increasing the AC resistance of the conductor and increasing losses. In engineering, the distance from the conductor surface to a current density of 1/e=0.368 of the conductor surface is defined as the skin depth.
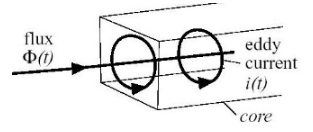
Schematic diagram of vortex generation
From the above, it can be seen that increasing the current and frequency can increase the heating effect, causing the heated object to quickly heat up. Therefore, induction power supplies usually need to output high-frequency high current.
Induction heating power supplies are divided into two types based on compensation forms: parallel resonant (current type) power supplies and series resonant (voltage type) power supplies.
The inverter used in parallel resonant power supply is a parallel resonant inverter, and its load is a parallel resonant load. Usually, a current source is required for power supply. In induction heating, the current source is usually assumed to have a fixed input current at the inverter. By alternately turning on and off the controllable period on the inverter, an alternating anti wave current can be obtained at the output of the inverter. The current replication depends on the input current value of the inverter, and the frequency depends on the switching frequency during the period.
The inverter used in the series resonant power supply is a series resonant inverter, and its load is a series resonant load. Usually, a voltage source is required for power supply. In induction heating, the voltage source is usually composed of a rectifier and a large capacitor. Due to the large capacitance value, it can be approximately assumed that the input voltage of the inverter is fixed and unchanged. By alternately turning on and off the controllable period on the inverter, an alternating square wave voltage can be obtained at the output of the inverter, whose voltage amplitude depends on the input voltage value of the inverter and the frequency depends on the switching frequency of the device.
The difference between series resonant inverters and parallel resonant inverters lies in the different oscillation circuits they use. The former uses L, R, and C in series, while the latter uses L, R, and C in parallel;
During the commutation process of a series resonant inverter, the thyristor is naturally turned off, and the current gradually decreases to zero when turned off, resulting in a short turn off time and low losses. During commutation, the turned off thyristor is subjected to back pressure for a long time.
During the commutation process of a parallel resonant inverter, the thyristor is forced to turn off during full current operation. After the current is forced to drop to zero, a period of back pressure time is required, resulting in a longer turn off time. In contrast, series resonant inverters are more suitable for use in induction heating devices with higher operating frequencies.
Series resonant inverters are easy to start and suitable for workplaces with frequent startup; However, parallel resonant inverters require additional start-up circuits, making start-up more difficult and time-consuming. Some people are still studying the starting problem of parallel resonant inverters.




















